reason
symptom
complication
treat
reason
- Spinal injury; ;
- Static and dynamic overloading of the spine;
- Improper load distribution on the spine;
- spinal mobility;
- strenuous physical activity;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Age-related changes.
clinical manifestations
- restricted activities;
- Lumbar curvature, "skew", scoliosis;
- muscle spasms;
- Lameness in one or both legs;
- Feeling of weakness, impaired sensitivity of the skin of the legs, weakened reflexes - compression of nerve endings.
diagnosis
- age-related changes
- spinal injury
- postural disorder
- Stachybotrys
- flatfoot
- genetic predisposition
- excessive exercise
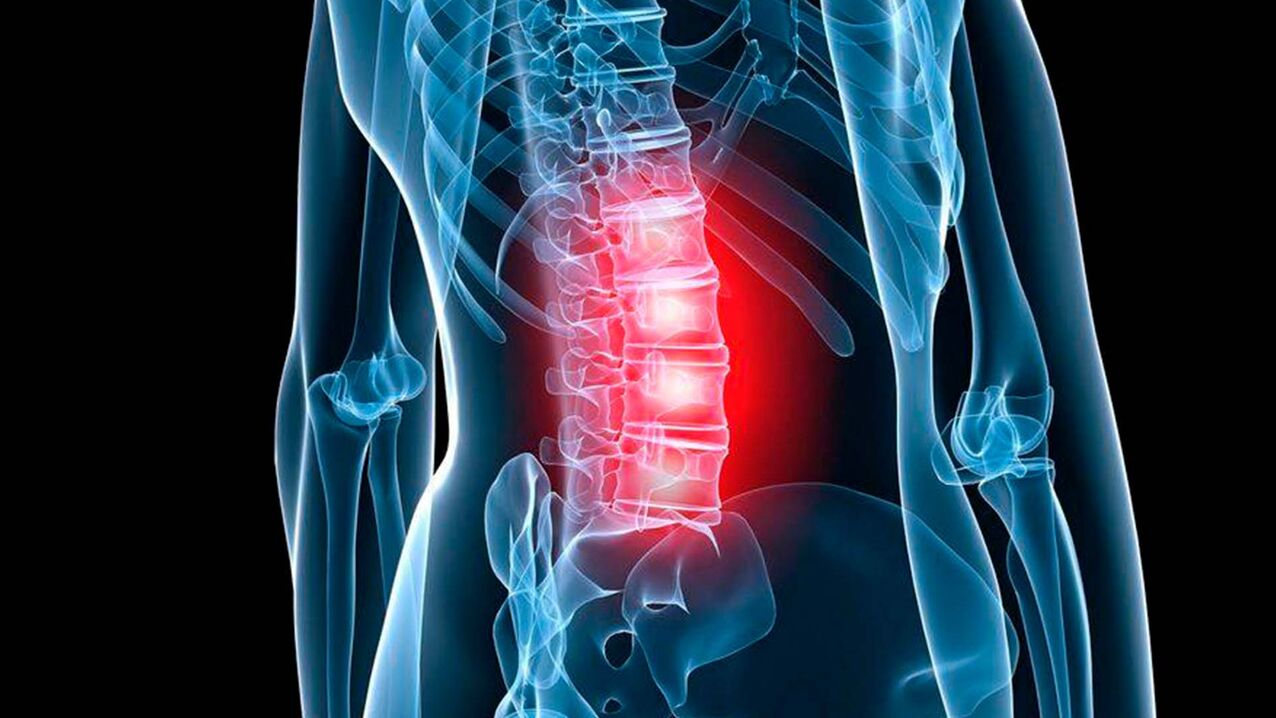
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Modern restorative medicine can greatly improve the condition of patients with lumbar osteochondrosis. Significant improvements can be achieved using a range of methods, including physical therapy, acupuncture, taking medications, therapeutic massage and more, with treatments based on individual prescriptions.
You can make an appointment by calling 8 (928) 337-60-60.
Lower back osteochondrosis
development stage
Development reasons
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
pain reflex symptoms
diagnosis
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Medication (Phase 1-2)
- Analgesics used to relieve pain: Topical (ointment, gel), oral (tablets, suspension), intramuscular (injection).
- NSAIDs prevent the development of inflammatory processes. Lower the temperature and eliminate swelling. Most often gels and tablets are used, in more severe cases (sciatic nerve inflammation) - injections. Prima courses are 7-14 days.
- Muscle relaxants. Use medication in the acute phase of muscle spasm and medication in the remission phase to consolidate the curative effect.
- Chondroprotectant. Prevents the destruction process of intervertebral discs, promotes regeneration, and improves the metabolism of cartilage tissue.
- Group B vitamin complex. Improve nerve conduction.
- Diuretics. Reduce swelling.
prevention
- An active lifestyle combined with moderate physical activity;
- Choose comfortable shoes or orthopedic shoes (if needed);
- weight control;
- sleep only on an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- Office furniture only has flat backs;
- Deny weight on the back and spine. When carrying heavy objects, the load should be evenly distributed between the hands.